Synthesis of lignin-derived materials provides an environmentally friendly alternative to common pesticide additives for plant development.
Your next plastic bottle could be made from sawdust
Researchers have found a way to make methoxyterephthalic acid, a precursor to commonly used plastics, from sawdust.
Microscopic nanowires of useful materials that grow themselves
Nanowires of exciting materials can be made via ‘electroless deposition’ – a technique that requires no complex templates or external energy input.
Pulling water out of thin air
Researchers have developed a new metal-organic framework that can harvest clean water directly from the air, even in arid climates.
Unexpected gold nanoparticles arise in ancient buildings through centuries of degradation
New research reveals plausible degradation pathways of metallic gold into nanoparticles through unforeseen corrosion!
Polymers efficiently extract water from air in arid conditions
A new and sustainable polymer gel unlocks water capture efficiencies never seen before!
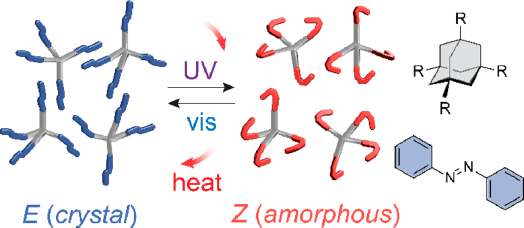
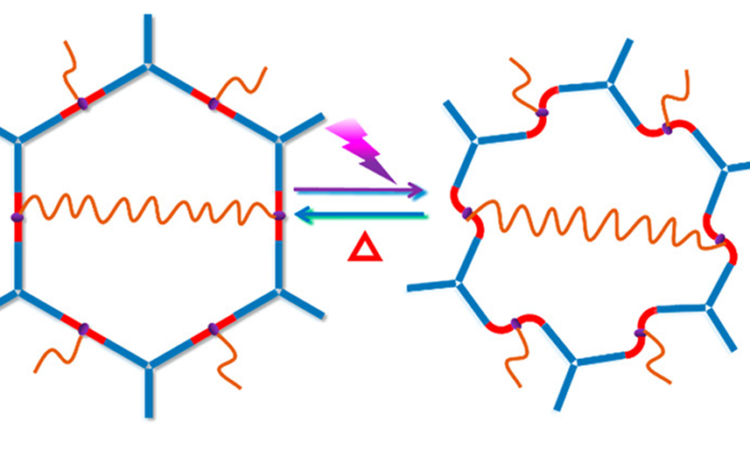
Sunlight to heat: New solid materials store and release solar energy by rotating bonds
A new class of light-absorbing solids isomerizes to store light energy as heat.
A Peek Inside a Fast-Charging Battery
Researchers can now watch what happens to particles inside a battery in real time.
Wearable electronic patches detect biomarkers of human health using plasmonic material
Research in wearable electronics brings us closer to personalized medicine with plasmonic materials.
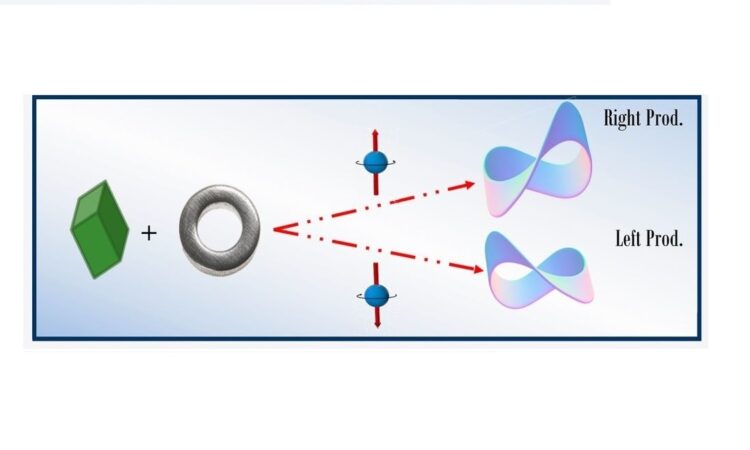
Electron spin selectivity effects can be harvested in asymmetric catalysis
A deeper understanding of spintronics enables the generation of new technologies using chiral molecules.
Cheap Molecule Could Lower the Cost of Batteries
A electroactive anthraquinone has been inexpensively designed with a reasonable but not record breaking stability in redox flow batteries.
Greener materials for the next generation of solid fuels
Greener materials and processes for fuels and explosives! Scientist demonstrate how to tune a class of porous materials that ignite spontaneously when mixed with acid.
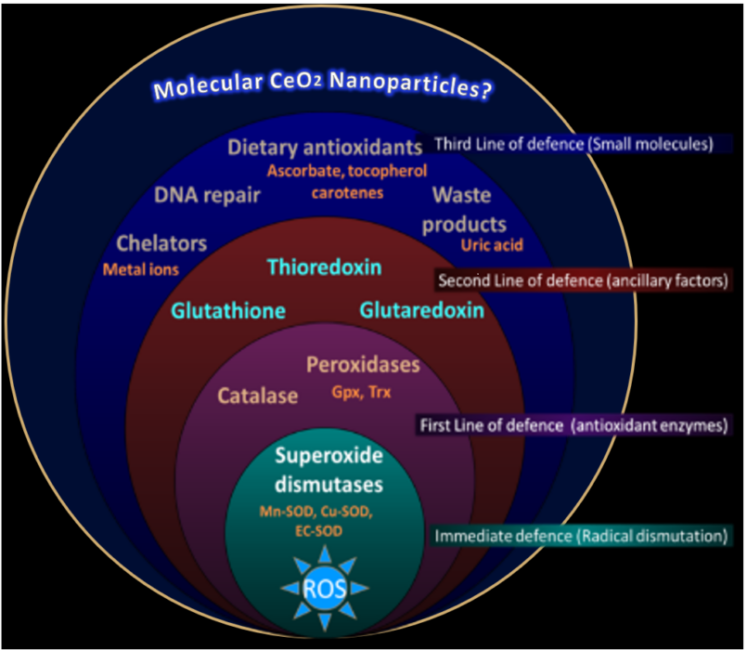
Molecular Nanoparticles: Large Molecules to Prevent Oxidative Stress?
Maybe chemistry can save us—in this case, synthetic chemists have developed a family of lanthanide-oxo molecules and investigate their capabilities as radical species scavengers, with a possible future in the clinic to mitigate various diseases onset by oxidative stress (get antioxidants into your diet, people!).
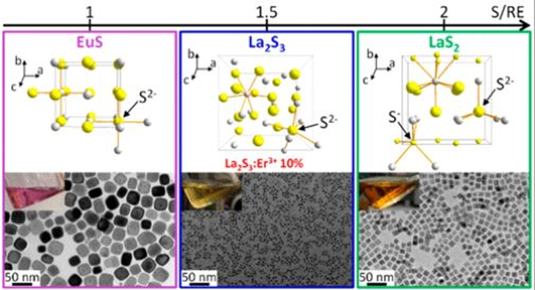
Engineering new types of nanocrystals through ingenious chemistry!
Scientists access new types of nanocrystals by leveraging simple acid-base concepts. The take-home message: always remember the basics!
Looking into the crystal bubble
Protein crystallisation is an important technique in drug discovery, and storage of proteins in the biopharmaceutical industry but can sometimes be regarded as a dark-art. Read how researchers use air-bubbles to improve protein crystal growth.
What gives bird feathers such vivid colors?
Birds have a unique way of creating color in their wings and this is how they have become so colorful.
Affordable and efficient carbon capture using nano-scale sheets in larger membranes
Metal-organic framework additives to membranes improve the efficiency of carbon capture by 9x, and are less expensive as well!
EFFICIENT CHEMISTRY BEHIND THE OLED SCREENS
OLEDs are earth-friendly, energy-efficient, all while being ultra-thin, flexible, and lightweight. They are the future of ultra-efficient lighting. Researchers are now coming up with new techniques to fabricate such sustainable and efficient OLEDs.
Revolutionize energy, agriculture, and the environment—in the most ap-peel-ing way
Biochar may be one of the most multi-talented materials in existence—do you know what your leftover orange peels are capable of?
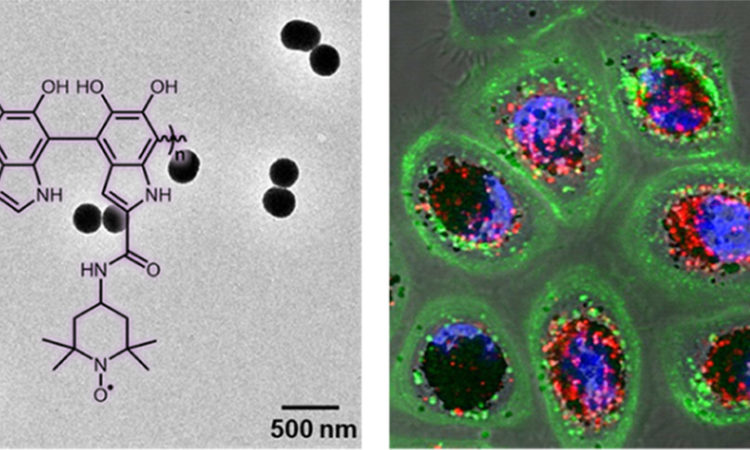
Melanin nanoparticles to better protect our cells
How does melanin protect cells from damaging radiation? How can this ability be improved?
Monitoring Vital Signs with Temporary Tattoos
Skin-conforming, ultra-thin wearable medical sensors could make going to the doctor less invasive than ever before. This newly developed, “tattooable” sensor uses a newly developed material to create one of the thinnest yet.
Catching it Early: New Ways of Detecting Coronavirus
Coronavirus has affected every one of us directly or indirectly. Early detection can lower the spread of the disease. Let’s learn about a new technique for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19.
How effective are fabric masks?
The COVID-19 global pandemic has affected nearly every aspect of our lives, including the daily use of face masks. But how well do home-made fabric masks really filter the air we breathe?
These artificial muscles don’t mind being “light” weight
Light-responsive substances are all the rage; find out how one research group invented a new class of photomechanical materials.
Hydrogenation without turning up the heat
Researchers discover a new way to dope high-melting oxides in solution with hydrogen.