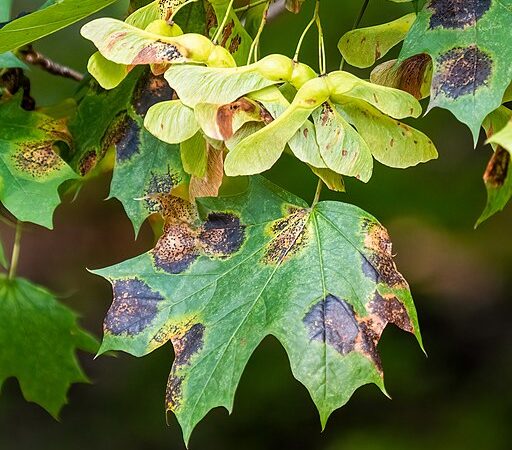
Scientists create a variety of chemical compounds and a new leaf test to investigate how the A. alternata fungi infects only the Asian pear.
Drug chaperones stop proteins before they aggregate
Scientists design new molecular chaperones that can capture aggregating proteins before they cause neurodegenerative damage.
Electrified nanopipettes decrease diagnostic time for amyloid diseases from days to hours
Researchers at the University of Montpellier develop a diagnostic test for Parkinson’s disease with a glass pipette and electric current that’s quick, accurate and inexpensive.
Chemists figure out how the grass pea makes its BOS neurotoxin
One of the most abundant South Asian and Sub-Saharan African legumes is the hardy, nutritional grass pea. However, the vegetable naturally produces a paralyzing neurotoxin, and the exact mechanism has long eluded scientists – until now.
Identifying toxic pesticides with microbial electricity
Some pesticides function similarly to the nerve agent sarin, and their ubiquitous use makes them a constant health hazard if unmonitored. Chemists designed a dual-microbe sensor to selectively and sensitively determine when the hazardous chemicals are nearby.
Outsmarting the cancerous activity of cathepsin B with pH-selective peptides
Scientists showed that by modulating cathepsin B’s cleavage activity with pH-selective peptides, they can irreversibly and selectively stop its cancerous activity.
Molecular tweezers pick viral membranes apart
While most scientists search for specific treatments for viruses like Ebola, Zika and SARS-Cov-2, non-specific methods can have broad impact. Researchers from the United States and Germany joined forces to make molecular “tweezers” that pick apart viruses to death.
Boiling mulberry juice increases its anti-cancer properties
Black mulberry juice is a known antioxidant – compounds that can consume free radicals before they can harm your cells. Researchers at Guangdong University also show that boiling mulberries increases its ability to treat colon cancer in cell culture, but not through antioxidant mechanisms.
#BlackInChem: Creating Support and Community for Black Women in STEM
Devin Swiner, one of the founders for #BlackInChem, shares what’s she’s learned, the hard-won wisdom she has earned as a Black woman in analytical chemistry.
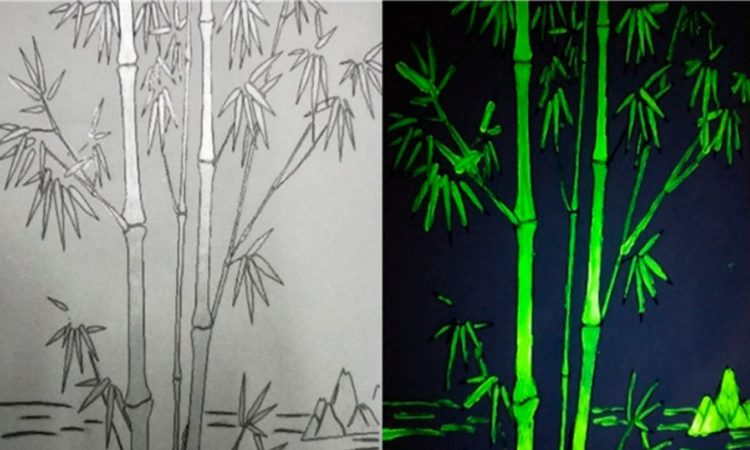
Monitoring plant maturation with a Wack reaction
When the authors’ blurb about their own work is “Okay, bloomer,” you know you have to read it.
Want fluffy whole wheat bread? Use smaller flour particles
Chemists take a gander at how to make more appealing whole wheat loaves. For your COVID-19 baking needs and beyond!
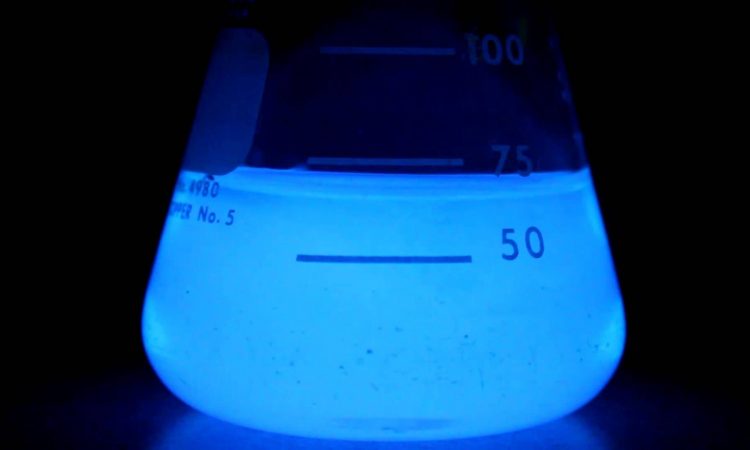
Make it green, make it bright!
Scientists craft a “greener,” copper-iodide-based ink with amazingly efficient photoluminescent properties
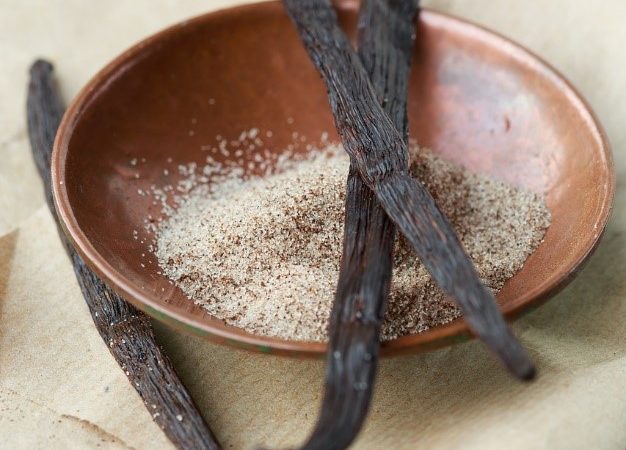
Vanilla substitute loosens up cell membranes to increase drug uptake
Could vanillin, the flavoring molecule extracted from vanilla bean, increase our body’s ability to absorb ingested drugs?
Detergents are for more than washing dishes
Studying membrane-bound proteins requires stabilizing their structure outside of the membrane – otherwise they fall apart. But our analytical techniques have not risen to the challenge. Sadaf et al. pushes us forward by developing novel detergents for stabilizing membrane proteins.
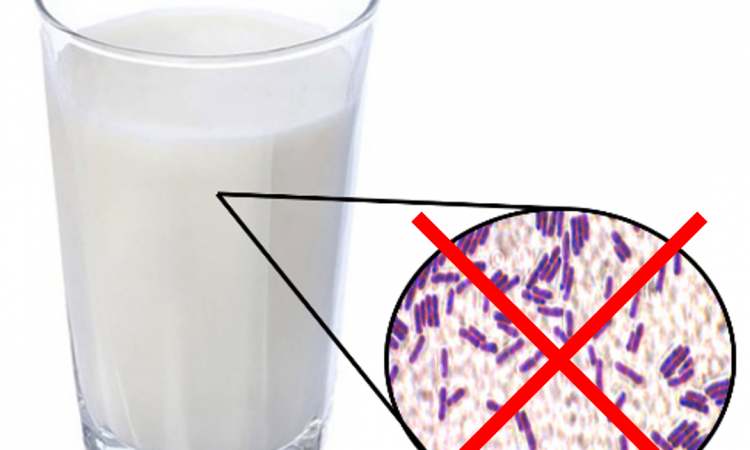
Now slide real smooth: Using peptide coatings to prevent biofilm formation
When it comes to milk, preventing bacterial contamination on dairy equipment is key. Researchers in Israel developed a biological coating to prevent biofilm formation and keep their moo-juice fresh and clean.
Delicious diagnosis – real-time glucose analysis straight from your gut
Scientists from UCSD and Compultense University developed non-invasive tools to measure gastrointestinal distress, monitoring chemical markers in real-time.
Light me up: can visible light impact forensic luminol reactions?
Crime scene techs use luminol to reveal latent bloodstains – can normal, visible light increase the reaction’s sensitivity?
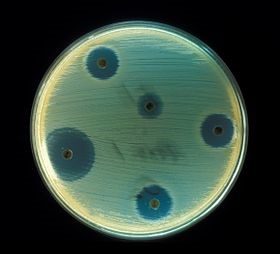
Manipulating actinomycetes for unusual antibiotics
Scientists genetically modify bacteria to overproduce uncommon antibiotics, revealing information on how bacteria regulate and modify its metabolites.
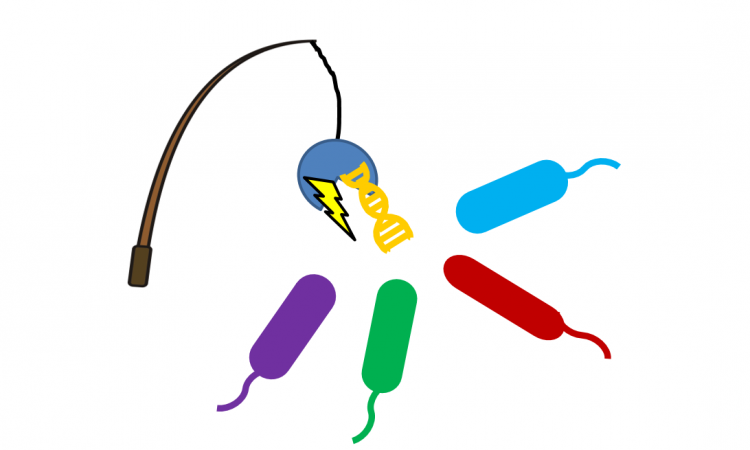
Fishing for bacteria with gold and DNA
What happens when you bring DNA strands, gold nanoparticles, conformation-induced color changes, and a highly-intrusive bacterium together? A field-portable, inexpensive test for the world’s greatest bacterial threats.