Researchers meld ideas from biology and chemistry to generate hybrid catalysts that can catalyze natural reactions at even faster rates.
Lighting the way: Molecular beacon provides high-res images of Alzheimer’s protein cleavage
The onset of Alzheimer’s disease is still not well understood. Researchers have developed a high-resolution visualization technique that could lead to improved treatment outcomes. Check it out!
No More Burnt Bridges: DNA Nanoengines Designed to Perform Multiple Cycles
The authors here present the next step in artificial nanoengines – an engine that can perform multiple cycles over the same path.
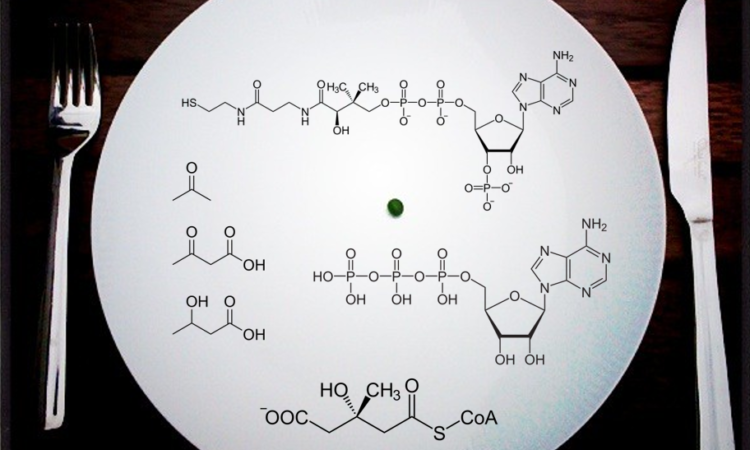
The Chemistry of Intermittent Fasting
Our bodies evolved two primary systems to generate energy so why is one so misunderstood?
New Genetic Codes to Program Biology
Researchers show for the first time that “unnatural” codons can code for “unnatural” proteins within a cell. Organisms can now operate with both synthetic code and synthetic hardware!
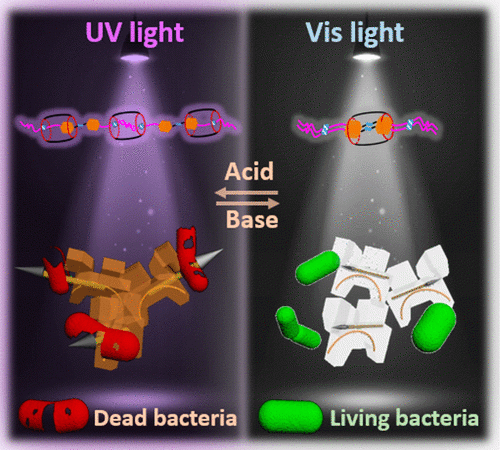
It’s Alive! 3D Printed Living Materials with Antibiotic and Wounding Healing Abilities
Inspired by nature, researchers at MIT have printed the soil bacteria, Bacillus subtilis, into polymer gels to create a living material with the ability to heal wounds and eliminate the highly infectious bacteria Staphylococcus Aureas. Check it out!
“Trojan Horse” Antibiotics: New Weapons for the Battle Against Drug Resistance
How do scientists fight back against drug resistance? Today’s Chembite focuses on promising developments with antibiotics using “trojan horse” tactics to trick bacteria!
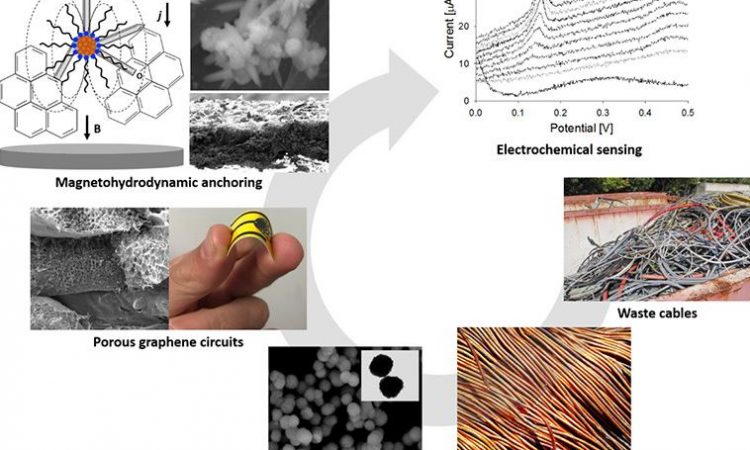
Common Sense Recycling – Turning Waste Cables into Electrochemical Sensors
Modern technology is evolving at a mind-blowing rate, but what should we do with all of the obsolete hardware? Researchers are finding clever ways of recycling the old material – check it out!
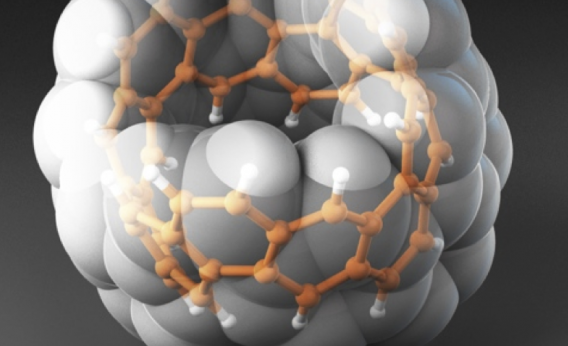
A New Duo in Catalysis: Combining Gold Nanoparticles with Enzyme Compartments
Biological catalysts and inorganic catalysts each have their own advantages and it is sometimes difficult to choose one or the other. So why not combine them into a powerful hybrid catalyst? That’s exactly what the researchers did in this recent article from ACS Catalysis.
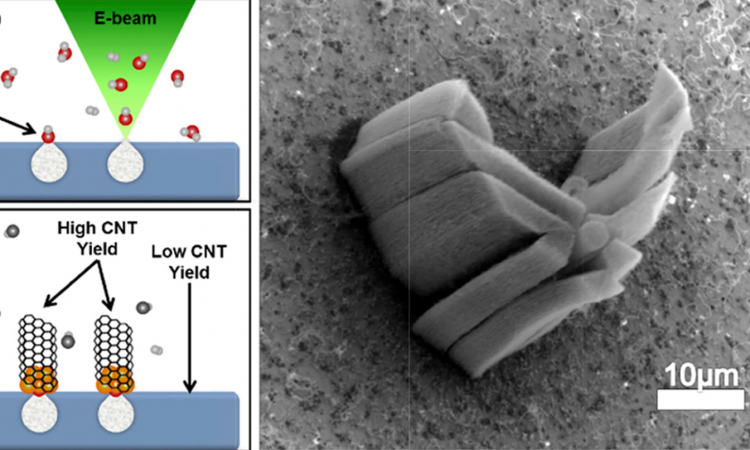
Printing Carbon Nanotube Patterns Using Electron Beams
Carbon nanotubes have material properties straight out of a science fiction novel. Yet, it is still difficult to assemble carbon nanotubes into organized structures where the science fiction-like properties can really shine. Discover what researchers are doing to solve this problem!
5 Facts About Catalysts You Might Not Know
Catalysis is a common chemistry concept, but there are many intricacies involved. Check out some of these lesser-known facts!
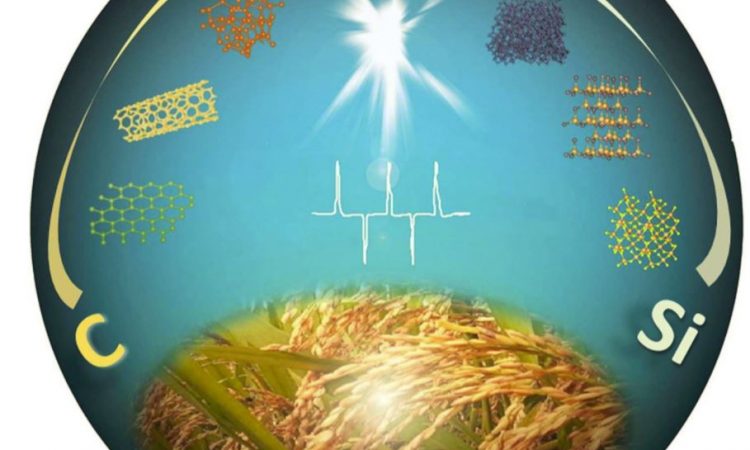
Going against the grain: Turning rice husks into batteries and solar cells
Discover how rice husk be converted into structures like carbon nanotubes and lithium battery anodes!
Engineered Fungus is a New Source for Polymer Building Blocks
They gave us beer, bread, and cheese – now microorganisms make the building blocks of new polymers.
Hitting the Jackpot – Evolving Artificial Biocatalysts Through Randomization
Random change has been powering life’s evolution for billions of years. Can it also power the evolution of artificial biomolecules?
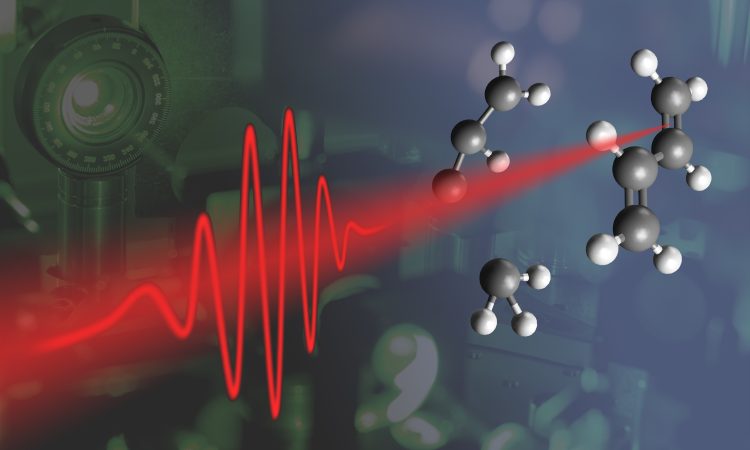
Set phasers to stun: Accelerating chemical reactions with precise IR laser pulses
Heating a chemical reaction to accelerate the reaction rate is like setting phasers to kill, it may get the job done but it’s certainly not the most elegant or effective method. What if you could provide just enough energy to break the appropriate bonds and control exact product outcomes without wasting energy?
Synthetic Biology and Synthetic Chemistry Join Forces
By tailoring mild synthetic chemistry methods to be compatible with living systems, these researchers have made artificial biochemical reactions a reality.
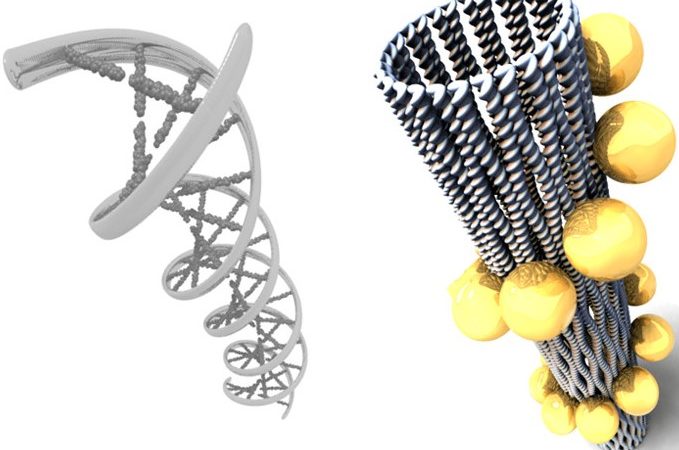
Assembling Gold Nanoparticles into 3D Structures Using DNA
How can DNA be used to enhance applications in nanotechnology? The authors here create never-before-seen optical systems by combining DNA origami with plasmonic nanoparticles.
Buckle Up: The Nanobelt has Arrived
What’s so special about a nanobelt? Let’s find out.
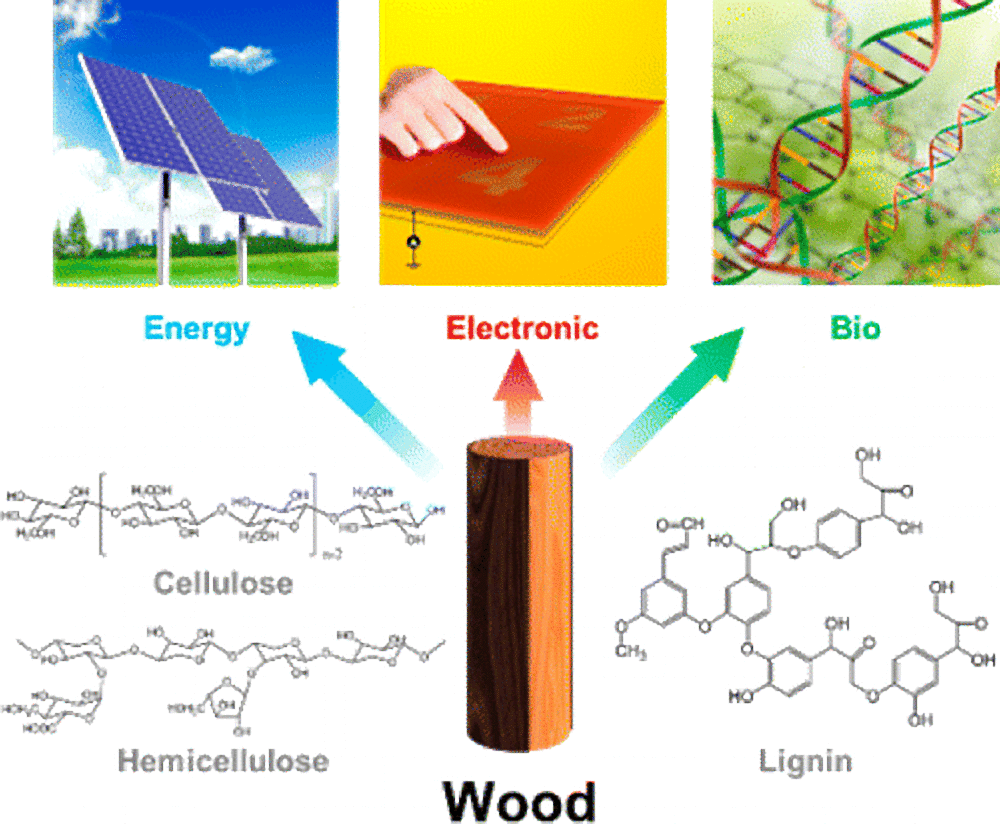
Beyond paper and furniture: Modern chemical applications of wood
How can chemists use wood to make blue jeans blue and parachutes strong? Check it out!
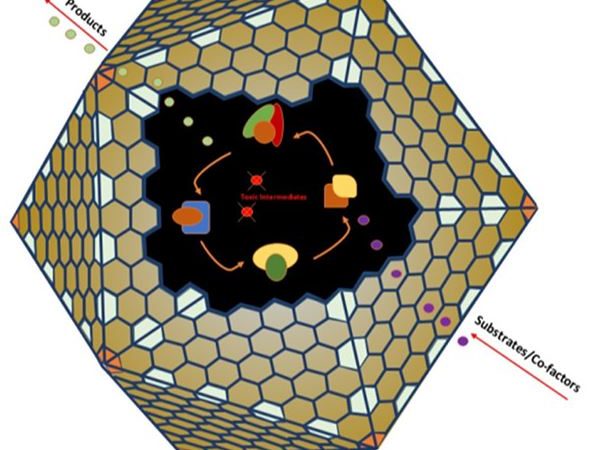
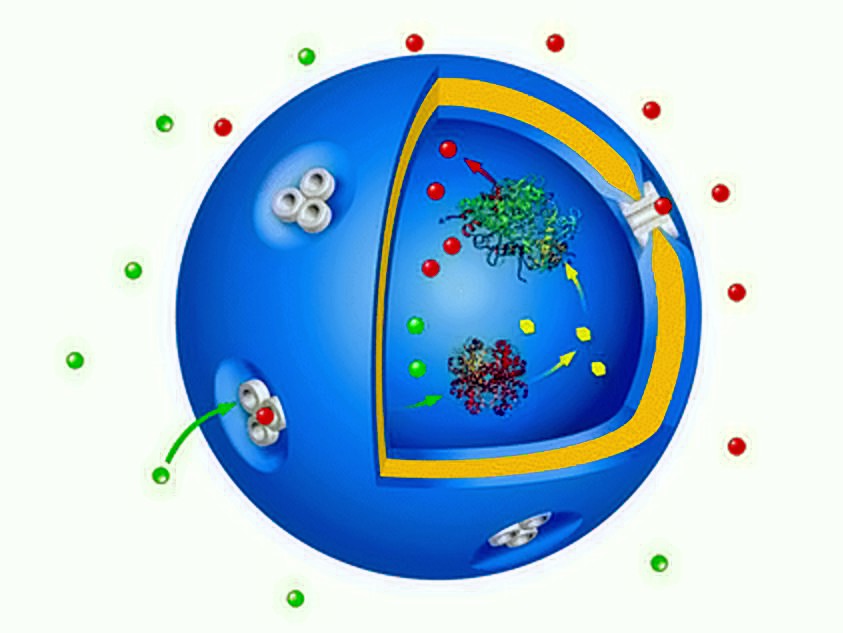
Nanoreactors for Enzyme Cascades
What are nanoreactors and how can they enhance multi-enzyme reactions? Let’s find out!
Nature Does It Best! – Engineering New Catalysts Using Evolution
As versatile as enzymes already are, it’s actually possible to engineer enzymes to catalyze reactions that are entirely new to nature!
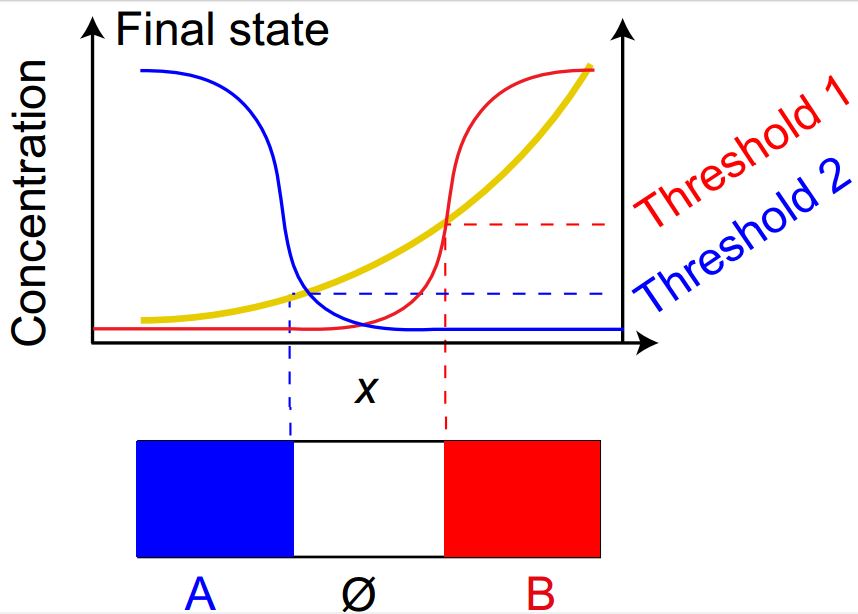
Patterning World Flags and More with DNA
Using similar principles to those that guide embryos in early development to form different organs and tissues, this research could lead to artificial objects that are capable of patterning themselves into many different complex structures.
Listen and Grow! – The Story Behind Growing Polymers with Sound
Our bones have the ability to heal themselves when exposed to mechanical stresses by forming new polymeric material, so what’s stopping scientists from doing the same synthetically?
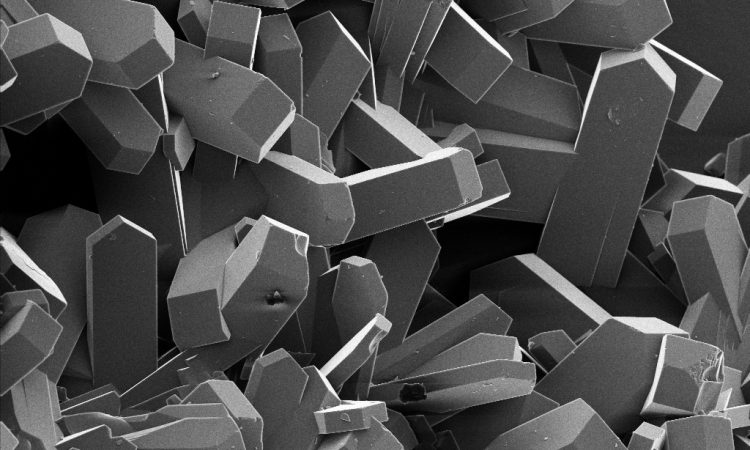
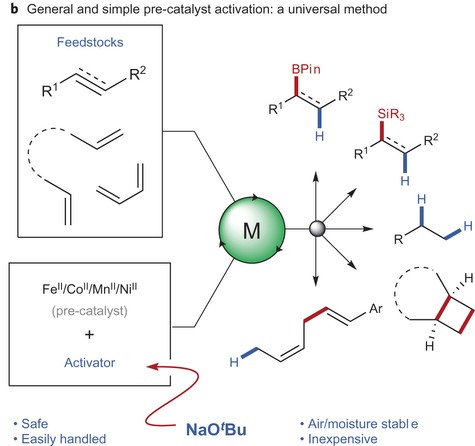
A Simple Approach for Developing Inexpensive and Sustainable Metal Catalysts
In order to keep catalyst-based industries sustainable and profitable, new catalysts need to be developed that utilize inexpensive, earth-abundant materials. The authors here present a novel method for easily forming stable earth-abundant metal catalysts, which are inexpensive and sustainable alternatives to precious-metal catalysts.
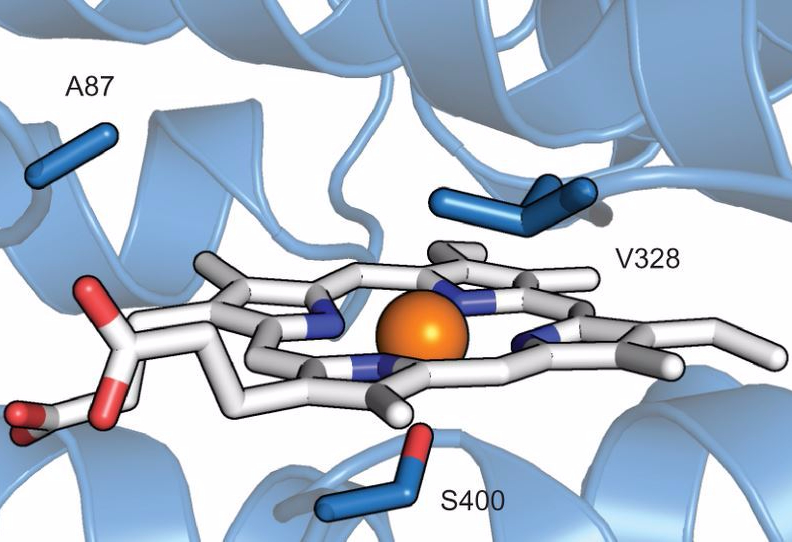
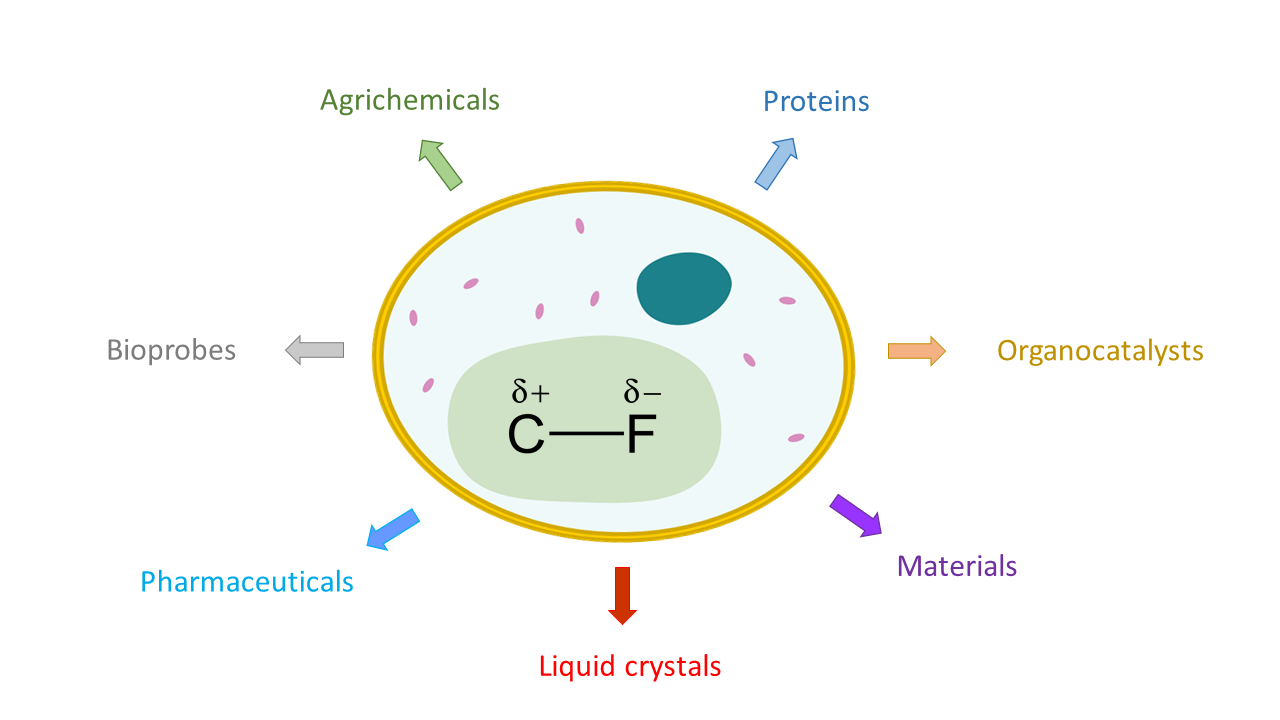
Using Biology to Harness the Power of Fluorine Chemistry
What comes to mind when you think of fluorine? The sodium fluoride in toothpaste and mouthwash is the typical, everyday example that most people think of, but fluorine plays a large role in many other compounds. Pure fluorine is a highly reactive and poisonous gas, while fluorinated compounds are incredibly stable, fairly nontoxic, and used in many real-life applications.