Repurposing the Inverse Electron Demand Diels Alder chemistry to create robust DNA-based devices that operate effectively within living cells.
Fungi use a specific chemical group to hijack the immune system of their plant prey
Scientists create a variety of chemical compounds and a new leaf test to investigate how the A. alternata fungi infects only the Asian pear.
Drug chaperones stop proteins before they aggregate
Scientists design new molecular chaperones that can capture aggregating proteins before they cause neurodegenerative damage.
From Code to Fold – Potential of DNA in Crafting Protein Mimics
By leveraging different DNA scaffolds as templates, with variations in subunit numbers, peptide orientations, and organic junctions, researchers gain unprecedented access to untapped peptide sequence spaces.
Understanding how diverse bile acids are recognized
Characterizing gut microbial enzymes
Discovery of a promiscuous halogenase
Discovery of new halogenases from marine bacteria
Smile Big!… An Interesting Family of Compounds Can Help Fight Periodontal Diseases
Smile Big! Researchers have developed new compounds that could help fight periodontal diseases.
Electrified nanopipettes decrease diagnostic time for amyloid diseases from days to hours
Researchers at the University of Montpellier develop a diagnostic test for Parkinson’s disease with a glass pipette and electric current that’s quick, accurate and inexpensive.
Discovery of gut microbial enzymes that modify drugs
Scientists uncover more ways gut microbes modify drugs
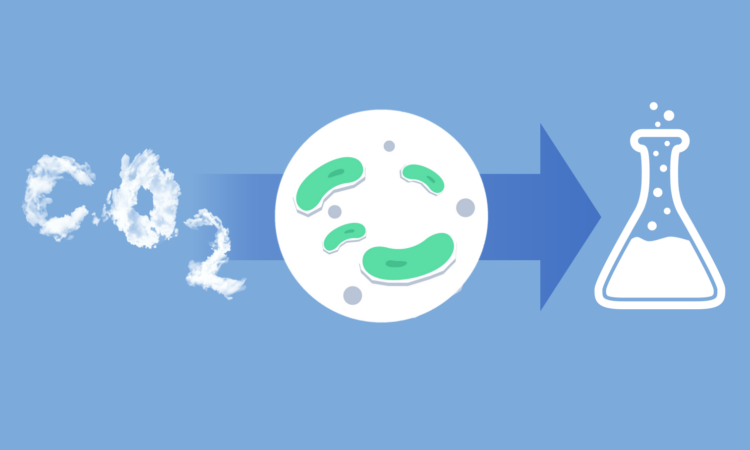
These Engineered Microbes Recycle Greenhouse Gases to Combat Climate Change
Scientists showcase a new, large-scale method to convert harmful greenhouse gases into commercially lucrative chemicals.
Wearable electronic patches detect biomarkers of human health using plasmonic material
Research in wearable electronics brings us closer to personalized medicine with plasmonic materials.
Chemists figure out how the grass pea makes its BOS neurotoxin
One of the most abundant South Asian and Sub-Saharan African legumes is the hardy, nutritional grass pea. However, the vegetable naturally produces a paralyzing neurotoxin, and the exact mechanism has long eluded scientists – until now.
Non-invasive, low molecular weight, biomarker method for detection of skin cancer.
Development of a new, non-invasive and topical sampling method uses low molecular weight, skin cancer biomarkers for better detection for early stages of skin cancer diagnostics.
Go Ask Mother Nature—she’s got an answer
An overwhelming majority of scientists are in agreement—and that never happens—something must change before we reach the so-called “point-of-no-return”. The onset of the industrial era (and the associated benefits) encouraged a system that pollutes our environment in search of the largest possible profits. More recently, our voices have gotten louder, and large groups of society have dedicated themselves to uncovering the solutions to these problems. Perhaps, in this regard, Mother Nature still has lessons to offer.
How to solve a structure
Combining different data to solve a structure
Identifying toxic pesticides with microbial electricity
Some pesticides function similarly to the nerve agent sarin, and their ubiquitous use makes them a constant health hazard if unmonitored. Chemists designed a dual-microbe sensor to selectively and sensitively determine when the hazardous chemicals are nearby.
Looking toward nature in the fight against COVID-19
How can we use compounds produced by cannabis as tools against COVID-19? This article discusses the identification of three cannabinoids which decrease the infection rate of SARS-CoV-2.
Unmasking COVID-19 infections
As the global COVID-19 pandemic rolls into its third year many of us wear masks almost all day at work or in the community. Read how these researchers have developed a sensor that can be embedded into your mask, which collects your exhaled breath to act as a COVID-19 test for the end of the day.
Going to Flavortown: Understanding the terpene content of cannabis
How can using computational and biochemical techniques help us understand the different flavors of cannabis? This paper explores identifying terpenes that make each cannabis strain unique.
Ozone Is The Key To Effective Lipid Detection And Isomer Resolution
Lipids are an important class of biological molecules where the physical and chemical structure will impact its function in our body. Effective lipid detection and analysis are key to understanding specific lipid interactions and overall biological impact. This paper discusses development of new analytical detection technique for mass spectrometry which provides greater insight into lipid biological chemistry.
Looking into the crystal bubble
Protein crystallisation is an important technique in drug discovery, and storage of proteins in the biopharmaceutical industry but can sometimes be regarded as a dark-art. Read how researchers use air-bubbles to improve protein crystal growth.
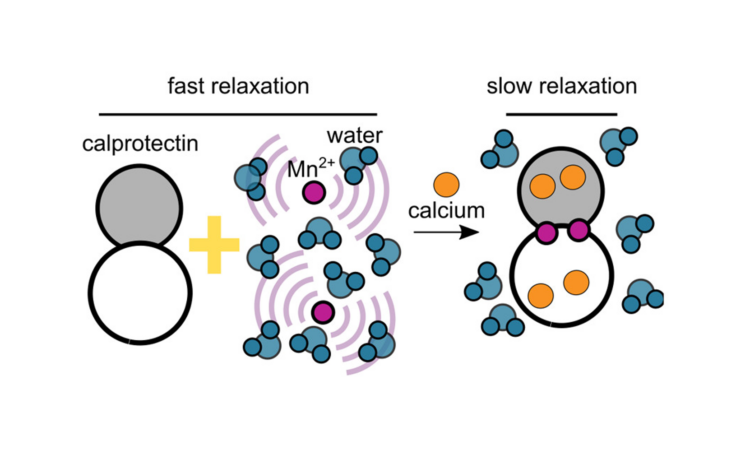
Where is the calcium? First steps toward a new MRI brain-imaging technique
Calcium is important in bones and in brains. But which brain regions have a lot of calcium? Do disease states affect calcium levels? A new tool is being developed to find out.
Outsmarting the cancerous activity of cathepsin B with pH-selective peptides
Scientists showed that by modulating cathepsin B’s cleavage activity with pH-selective peptides, they can irreversibly and selectively stop its cancerous activity.
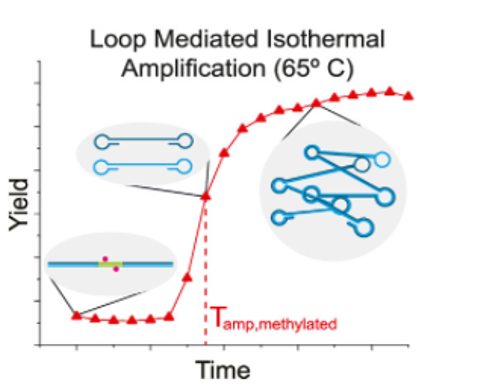
More than just genes: looking for disease markers in methylated DNA
A tiny methyl group (one carbon bound to three hydrogen atoms) can be a big marker for disease.
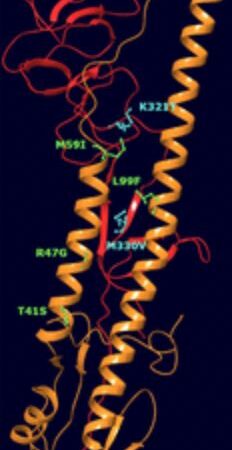
FINDING A DIVERSE ANTI-INFLUENZA MOLECULE
We will continue coming across new viral proteins and viruses, so it doesn’t hurt to be prepared for those. The work of White et al helps in giving a starting point for medicines against the Influenza viruses.