Development of a new, non-invasive and topical sampling method uses low molecular weight, skin cancer biomarkers for better detection for early stages of skin cancer diagnostics.
Go Ask Mother Nature—she’s got an answer
An overwhelming majority of scientists are in agreement—and that never happens—something must change before we reach the so-called “point-of-no-return”. The onset of the industrial era (and the associated benefits) encouraged a system that pollutes our environment in search of the largest possible profits. More recently, our voices have gotten louder, and large groups of society have dedicated themselves to uncovering the solutions to these problems. Perhaps, in this regard, Mother Nature still has lessons to offer.
Ozone Is The Key To Effective Lipid Detection And Isomer Resolution
Lipids are an important class of biological molecules where the physical and chemical structure will impact its function in our body. Effective lipid detection and analysis are key to understanding specific lipid interactions and overall biological impact. This paper discusses development of new analytical detection technique for mass spectrometry which provides greater insight into lipid biological chemistry.
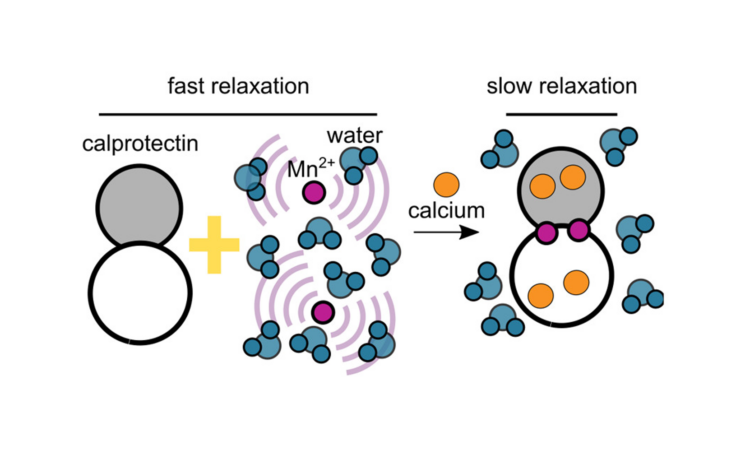
Where is the calcium? First steps toward a new MRI brain-imaging technique
Calcium is important in bones and in brains. But which brain regions have a lot of calcium? Do disease states affect calcium levels? A new tool is being developed to find out.
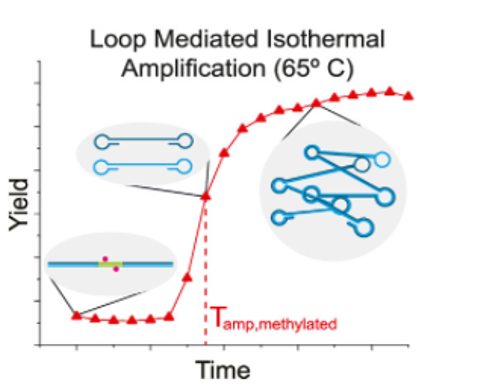
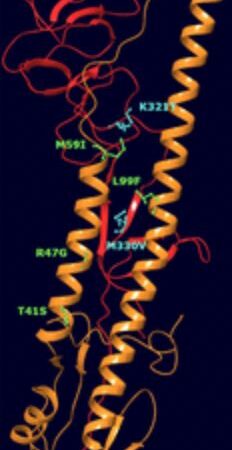
More than just genes: looking for disease markers in methylated DNA
A tiny methyl group (one carbon bound to three hydrogen atoms) can be a big marker for disease.
FINDING A DIVERSE ANTI-INFLUENZA MOLECULE
We will continue coming across new viral proteins and viruses, so it doesn’t hurt to be prepared for those. The work of White et al helps in giving a starting point for medicines against the Influenza viruses.
Upcycling Plant Matter
Avocado peels and uprooted invasive plants can become a source for anti-inflammatories. I’ll toast to that!
Working out what worked (or didn’t) in a work-up
In organic chemistry, once your reaction is over you generally “work-up” the mixture. But what happens if the work-up changes the outcome?
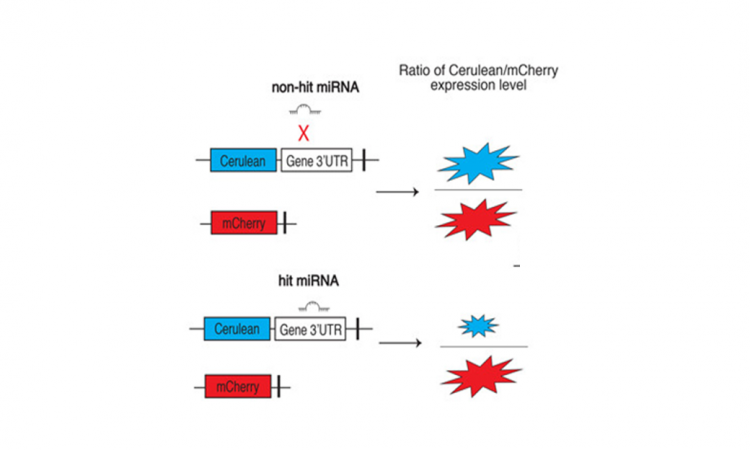
MicroRNAs: A New Assay Searches for Targets
If your DNA is a cookbook of “recipes” your cells could make, microRNAs help decide what’s for dinner.
Looking for Viruses in Wild Bats
Cataloguing viruses in bats and other animals may help predict or trace viral transmission to humans in the future.
Polishing a Drug Lead: A Replacement for Opioids Reaches Clinical Trials
Many molecules can decrease enzymatic breakdown of our body’s natural painkillers…but which one is fit to be the best new drug?
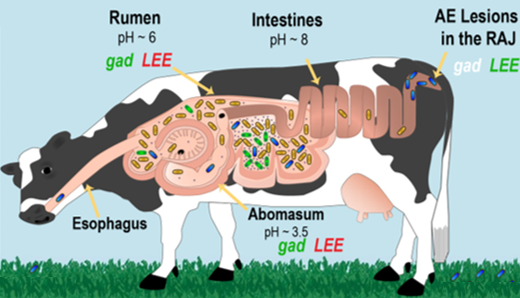
Pathogenic E. coli Can Survive Stomach Acid…For Now
Infected cattle can transmit E. coli to humans through contaminated ground beef, but scientists are looking for a solution.
Masked Entry – Increasing cell permeability of large molecules
Developing a drug that is able to enter the cell and interact with its target is no mean feat, especially for large molecules. Read about how this group ‘masked’ large molecules to improve their cell permeability.
Molecular tweezers pick viral membranes apart
While most scientists search for specific treatments for viruses like Ebola, Zika and SARS-Cov-2, non-specific methods can have broad impact. Researchers from the United States and Germany joined forces to make molecular “tweezers” that pick apart viruses to death.
The Smell of Rain Has a Biological Function
The earthy smell of soil originates from the bacteria that live there. But why do they produce this particular scent?
Life in the Hot Springs: Bacterial Tricks for Thermal Stability
When cooking an egg, heat denatures proteins in the egg. How does a thermophilic bacteria prevent its proteins from denaturing too?
Visualising Chemistry
Appreciating the 3D structure of the tiny chemical compounds we work with can be really difficult – but what if you could project the structure onto your living room floor?
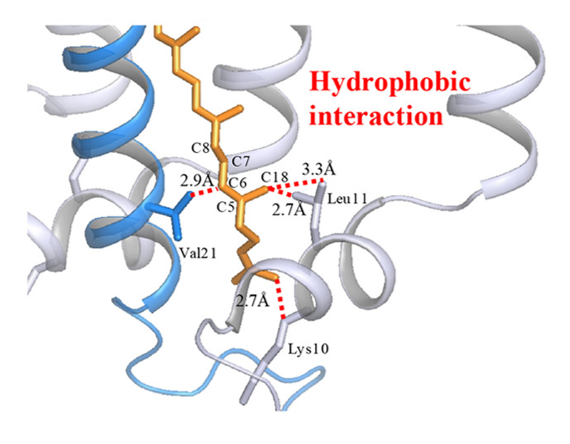
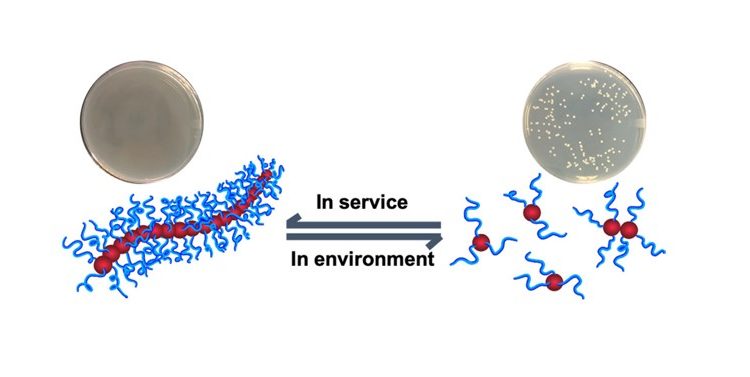
Better Antibiotics: Active in the Body, Degraded in the Environment
Antibiotics are lifesaving, but current practices don’t keep them from accumulating in the environment where they can damage nature and human health. A new antibiotic design aims to solve this problem.
Chemistry & COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic is consuming our news feed at the moment – while you’re self-isolating read about some of the great science research going on to combat our newest virus.
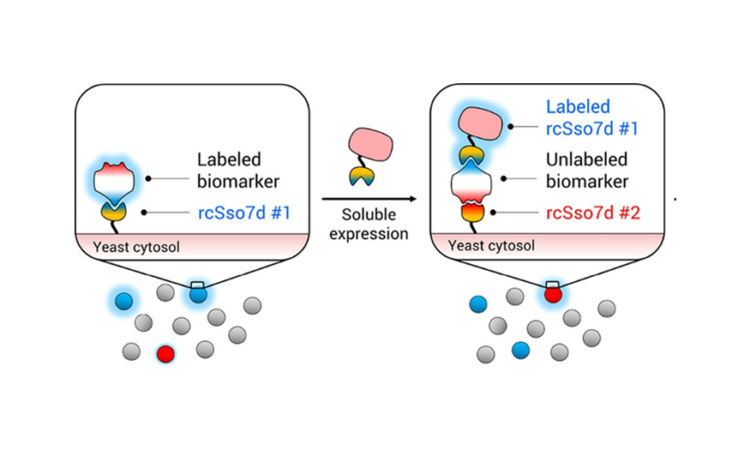
Rapidly Developing Disease-Specific Detection Methods
Antibodies in your body help fight disease by specifically targeting a viral or bacterial strain. This specificity makes antibodies useful for disease detection, but how do scientists reduce the chance of false positives and false negatives?
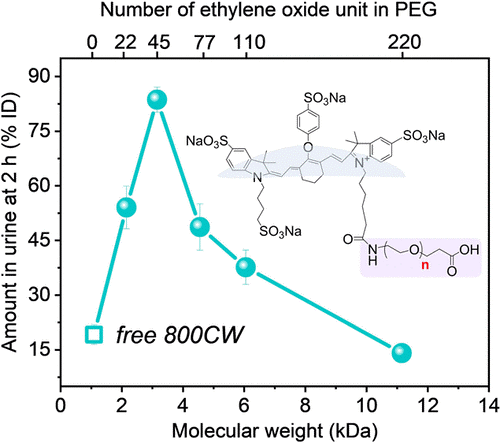
How Long Do Nanoparticles Stay in the Body?
As nanotechnology is developed into drugs for human health, scientists need to study nanoparticle clearance rates from the body.
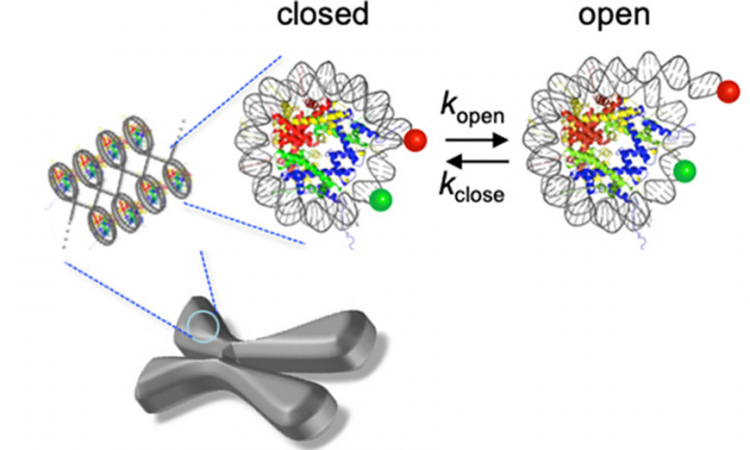
“Uncorking” a Mini Machine
Scientists discover a novel mechanism for taking apart tiny machines
More than just our genetic code: how chemical modifications affect gene expression
DNA is the instruction manual for how to produce an organism, one gene at a time. But our heart cells, liver cells, and brain cells are different, despite having the same DNA, thanks in part to the “epigenetic” modifications that control which genes are expressed.
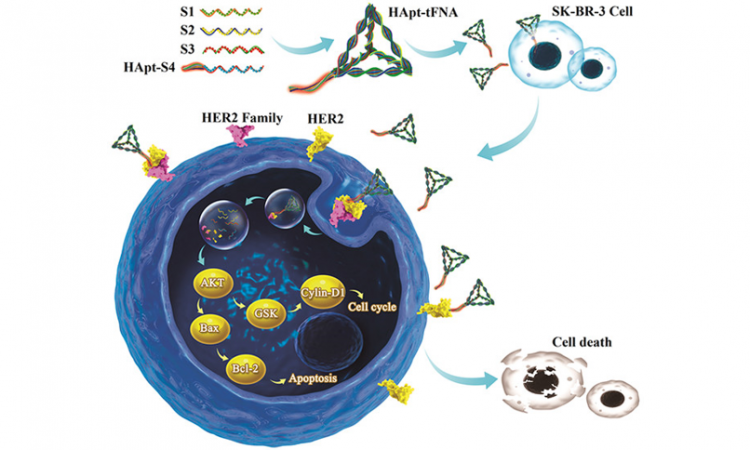
Nanoparticle Made of DNA Degrades Cancerous HER2 Protein
DNA can be more than just the genetic code. Can four specially designed strands of DNA destroy cancer cells?
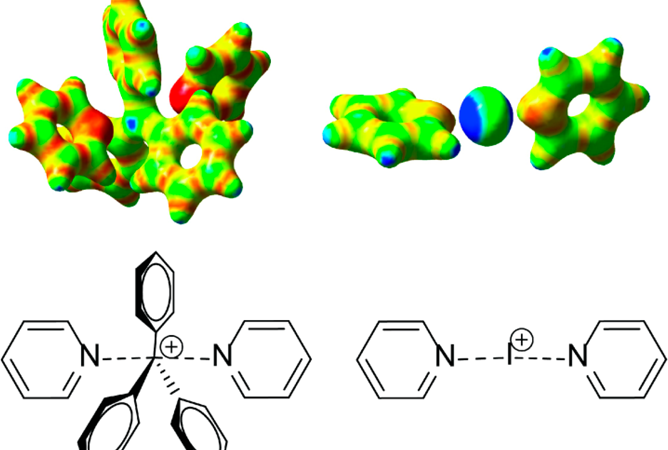
Filling the p-hole: Using a tetrel bond to better understand SN2 chemistry
Using a new model of a tetrel bond to further probe the mechanism of an SN2 reaction.