Hydrogen peroxide can be produced from water using green electrical energy, offering an environmentally friendly route to a vital material.
Unexpected gold nanoparticles arise in ancient buildings through centuries of degradation
New research reveals plausible degradation pathways of metallic gold into nanoparticles through unforeseen corrosion!
Electrified nanopipettes decrease diagnostic time for amyloid diseases from days to hours
Researchers at the University of Montpellier develop a diagnostic test for Parkinson’s disease with a glass pipette and electric current that’s quick, accurate and inexpensive.
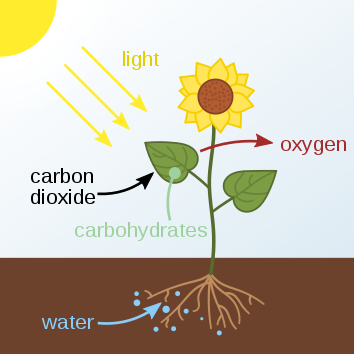
From harmful emissions to vital materials: how electrochemistry is making the most of carbon dioxide waste
Carbon dioxide can be converted into useful materials using electrochemistry. This is doubly advantageous, since we can stop carbon dioxide entering the atmosphere and also produce something useful that usually comes from fossil fuels.
A Peek Inside a Fast-Charging Battery
Researchers can now watch what happens to particles inside a battery in real time.
Go Ask Mother Nature—she’s got an answer
An overwhelming majority of scientists are in agreement—and that never happens—something must change before we reach the so-called “point-of-no-return”. The onset of the industrial era (and the associated benefits) encouraged a system that pollutes our environment in search of the largest possible profits. More recently, our voices have gotten louder, and large groups of society have dedicated themselves to uncovering the solutions to these problems. Perhaps, in this regard, Mother Nature still has lessons to offer.
Identifying toxic pesticides with microbial electricity
Some pesticides function similarly to the nerve agent sarin, and their ubiquitous use makes them a constant health hazard if unmonitored. Chemists designed a dual-microbe sensor to selectively and sensitively determine when the hazardous chemicals are nearby.
Biosensors from graphene-wrapped nanofibers
Using nanofibers to create biosensors decreases cost and wrapping them in graphene increases their conductivity.
Can chemistry overcome incompatibility?
A new way to have incompatible reactions occur in spatially separate regions of a liquid to create methanol from methane.
Monitoring Vital Signs with Temporary Tattoos
Skin-conforming, ultra-thin wearable medical sensors could make going to the doctor less invasive than ever before. This newly developed, “tattooable” sensor uses a newly developed material to create one of the thinnest yet.
Monitoring plant maturation with a Wack reaction
When the authors’ blurb about their own work is “Okay, bloomer,” you know you have to read it.
What a shock: material changes can impact charge
The amount of charging on an object changes when it is folded or unfolded.
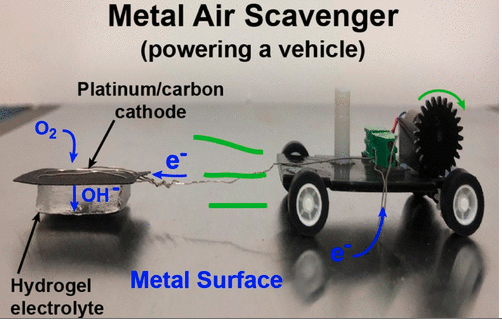
Metal-Air Scavengers Powering Tiny Robots
The smaller the robot, the harder it is to carry a fuel source around. That’s where these metal-air scavengers come in. Powered by oxidizing a metal surface, they could be a useful power source for the tiny robots of the future.
What happens when you add crap to graphene? Literally.
Graphene’s amazing properties make it one of the most popular new materials in recent years. But what if we could improve it with an unlikely additive?
What’s blacker than black?
There’s a new record holder for the world’s blackest material. Learn about how randomly oriented carbon nanotubes can be used to create a coating darker than anything else ever made!
Delicious diagnosis – real-time glucose analysis straight from your gut
Scientists from UCSD and Compultense University developed non-invasive tools to measure gastrointestinal distress, monitoring chemical markers in real-time.
The most promising artificial photosynthesis yet!
Researchers have designed a new way to convert CO2 into fuels that is efficient and cost-effective.
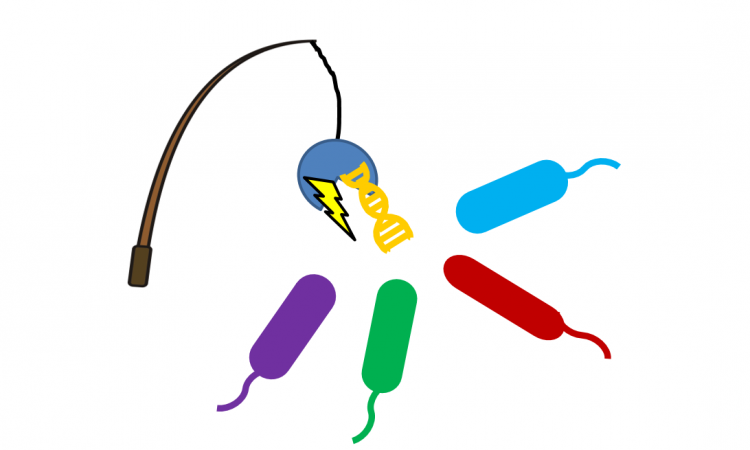
Fishing for bacteria with gold and DNA
What happens when you bring DNA strands, gold nanoparticles, conformation-induced color changes, and a highly-intrusive bacterium together? A field-portable, inexpensive test for the world’s greatest bacterial threats.
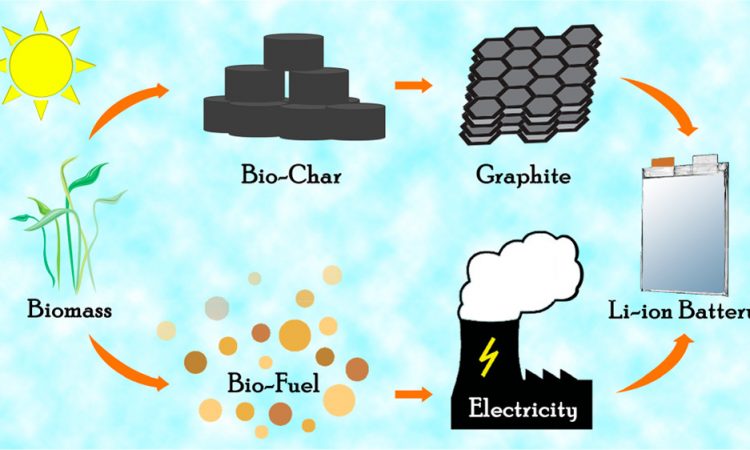
Making New Batteries Using Burnt Plants
We use lithium-ion batteries in our electronics every day, but getting the materials to build them isn’t very environmentally friendly. Let’s learn about a new way to recover one of these materials from burnt plants!
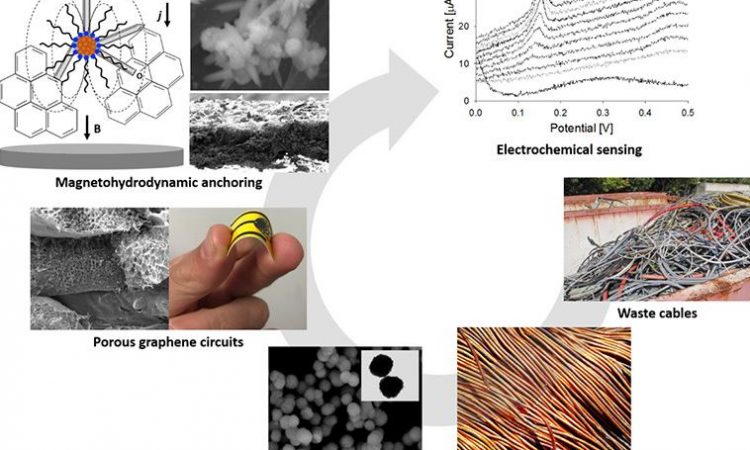
Common Sense Recycling – Turning Waste Cables into Electrochemical Sensors
Modern technology is evolving at a mind-blowing rate, but what should we do with all of the obsolete hardware? Researchers are finding clever ways of recycling the old material – check it out!
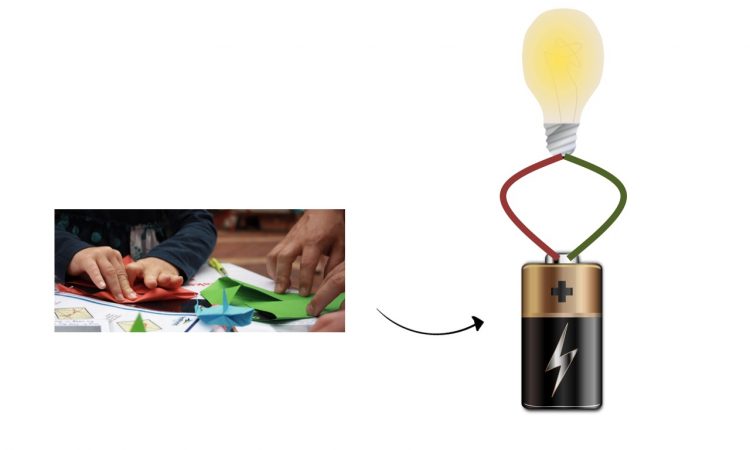
The Sci Art Collaboration that Powers Up!
Art could show the beauty of science. But art could also put science to work in real life!
Let’s learn from researchers about how origami can turn paper into a real battery!
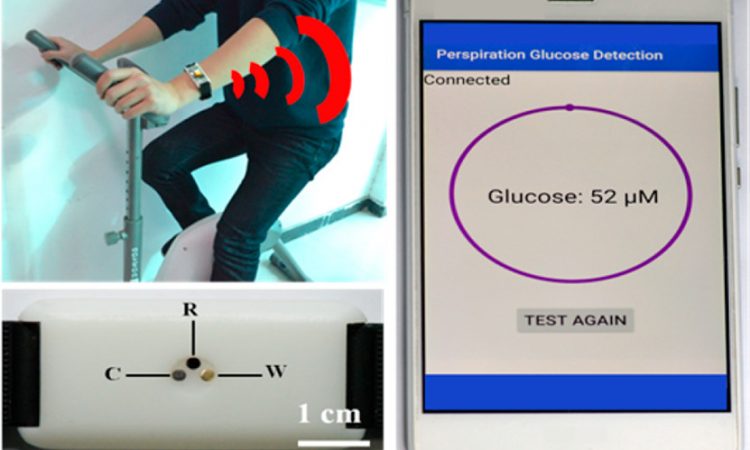
Monitoring Glucose Levels in Sweat with a Wearable Sensor
Measuring blood sugar levels by pricking your finger is painful and inconvenient. Learn about a new wearable device that measures your glucose levels with just your sweat!
Mood Lighting: Colorful Coatings for Smart Windows
Feeling blue? The chemistry of new “smart windows” could help – with a coating that adjusts to the outside temperature and a color filter that you can switch at will, they could be the perfect mood lighting for your energy-efficient home.
Weak Magnetic Fields Affect DNA Repair: A Migratory Bird’s Inner Compass?
Birds and other migratory animals use the Earth’s weak magnetic field to navigate, but what do they use as a compass? While previous research has uncovered some promising candidates, not until now have experiments identified a compass sensitive to fields as weak as Earth’s – DNA repair by photolyase.
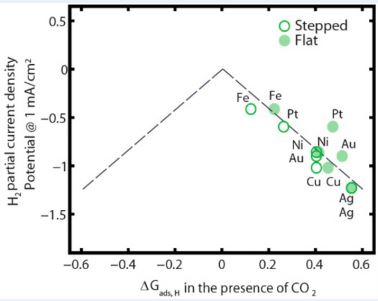
Intricate Balance of Carbon Dioxide and Hydrogen Adsorption for Catalysis
With metal catalysts, we can extract electricity from CO2 – reducing carbon emissions and creating renewable energy tech at the same time! There’s just one little problem, and it’s name is hydrogen…